Iran Mountains Map: Unveiling A Rugged Landscape Of Ancient Peaks
Iran, a land steeped in ancient history and vibrant culture, is perhaps most strikingly defined by its formidable topography. Dominated by rugged mountain ranges, an Iran mountains map reveals a landscape that is both breathtakingly beautiful and geographically significant, shaping the nation's climate, ecosystems, and human settlements.
These majestic peaks are not merely geological features; they are the backbone of the country, separating vast basins and plateaus, dictating weather patterns, and fostering unique biodiversity. Understanding the intricate network of Iran's mountains is key to appreciating its diverse environmental and cultural tapestry, offering insights into its rich geography and the resilience of its people.
Table of Contents
- The Dominance of Mountains in Iran's Topography
- The Mighty Alborz Range: Crown Jewel of the North
- The Expansive Zagros Mountains: A Spine Through the West
- Other Significant Mountain Chains
- Mountains Shaping Iran's Climate and Life
- Exploring Iran's Mountainous Regions: A Traveler's Guide
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Iran's Mountains
The Dominance of Mountains in Iran's Topography
Iran's landscape is profoundly shaped by its mountainous terrain, making it one of the world's most mountainous countries. Topographical maps showing the mountain ranges of Iran vividly illustrate how these rugged formations dominate the country's geography. The entire area of Iran can be broadly divided into four parts, with approximately half of the land consisting of mountains, while deserts and fertile plains each account for about a quarter.
- Alessandro Preziosi E Fidanzata
- Mt Bank Stadium
- Seo Young Joo
- Is Ice Spice Dating Anyone
- Westchester County Airport
This intricate network of ranges serves a crucial role: separating various basins or plateaus from one another, creating distinct geographical pockets across the nation. The populous western part of Iran is notably the most mountainous, characterized by formidable ranges such as the Zagros and Alborz mountains. These two major ranges, the Alborz in the north and the Zagros stretching from the northwest to the southwest, are the most prominent features on any Iran mountains map, defining much of the country's physical character.
The sheer scale and prevalence of these mountain systems mean that Iran's topography is incredibly diverse. From high peaks to deep valleys, the mountains create a dramatic backdrop for human settlement and natural ecosystems. They are not just barriers but also sources of vital resources, influencing everything from water distribution to agricultural practices across the country.
The Mighty Alborz Range: Crown Jewel of the North
The Alborz Mountain Range stands as a majestic natural barrier in northern Iran, running parallel to the southern coast of the Caspian Sea. This range is one of Iran's two major mountain chains, a defining feature on any comprehensive Iran mountains map. Its strategic location close to the Caspian Sea significantly influences the regional climate, creating a narrow strip of land along the coast that receives ample rainfall, contrasting sharply with the arid interior.
The Alborz is renowned for its dramatic peaks, deep valleys, and stunning natural beauty, attracting climbers, trekkers, and nature enthusiasts from around the globe. Its peaks are often snow-capped for much of the year, providing a striking visual contrast against the green lowlands of the Caspian region. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, the Alborz plays a vital role in Iran's water resources, acting as a watershed for numerous rivers and streams that flow into the Caspian Sea or the central Iranian plateau.
Mount Damavand: Iran's Highest Peak
Within the Alborz range lies its undisputed crown jewel and Iran's highest point: Mount Damavand. This dormant stratovolcano is not only the highest peak in Iran but also the highest in Western Asia. Standing at an impressive elevation of 5,609 meters (18,402 ft), it is also recognized as the highest volcano in Asia and the third highest volcano in the Eastern Hemisphere, surpassed only by Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Elbrus.
Damavand's conical shape, often capped with snow and ice, makes it an iconic landmark visible from great distances, including from Polour village in Amol. Its prominence and majestic appearance have made it a significant symbol in Persian mythology and literature. For climbers, Damavand presents a challenging yet rewarding ascent, offering breathtaking panoramic views from its summit. The mountain's volcanic nature also contributes to unique geological features and hot springs around its base, adding to its allure and ecological interest.
The sheer scale of Damavand underscores the ruggedness of Iran's topography, illustrating how a detailed Iran mountains map can reveal not just elevation but also the geological history and significance of such natural wonders. The mountain's towering presence serves as a constant reminder of the powerful forces that have shaped this ancient land.
The Expansive Zagros Mountains: A Spine Through the West
The Zagros Mountains represent the largest mountain range in Iran, forming a colossal natural barrier that stretches over 1,600 km (990 miles) from the northwest to the southeast of the Iranian plateau. This vast range is a dominant feature on any Iran mountains map, extending beyond Iran's borders into northern Iraq and southeastern Turkey. Its sheer length and breadth make it a critical geographical and ecological entity in the region.
The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border, covering a significant portion of the country's western and southwestern regions. Its rugged terrain is characterized by numerous parallel ridges and valleys, with many peaks surpassing 10,000 feet in elevation. This complex geological structure has resulted in a diverse landscape, from high alpine meadows to deep river gorges.
The range's geological history is marked by intense tectonic activity, leading to its distinctive folded and faulted appearance. This geological dynamism has also contributed to the formation of rich mineral deposits and oil fields, particularly in the foothills of the Zagros, making it economically significant for Iran.
Geographical Reach and Significance
The geographical reach of the Zagros Mountains is immense, impacting a vast swathe of land and influencing the climate and ecosystems of multiple countries. In Iran, the range is located to the northwest, extending close to the Persian Gulf, where its southern flanks meet the coastal plains. This proximity to the Gulf plays a role in regional weather patterns, influencing rainfall and temperature distribution.
The Zagros Mountains are not merely a physical barrier but a cradle of biodiversity and cultural heritage. The environmental variety supported by this range fosters distinctive ecosystems and agricultural zones throughout the country. Its varied elevations and microclimates allow for a wide range of flora and fauna, from oak forests in the wetter northern parts to more arid-adapted vegetation in the south.
Historically, the Zagros has been home to numerous ancient civilizations and nomadic tribes, whose way of life has been intricately linked to the mountains. The mountain range has facilitated trade routes and acted as a natural defense, shaping the demographic and cultural landscape of western Iran for millennia. Understanding the Zagros on an Iran mountains map is essential for grasping the historical movements and current distribution of Iran's diverse populations.
Other Significant Mountain Chains
While the Alborz and Zagros ranges dominate the Iran mountains map, the country's topography is further enriched by several other significant mountain chains. These ranges, though perhaps less extensive, play crucial roles in defining regional landscapes, climates, and human settlements. Iran's mountainous character is truly comprehensive, with rugged terrain found even in seemingly unexpected areas.
A series of massive, heavily eroded mountain ranges surrounds Iran’s high interior basin. These ranges act as a natural ring, separating the central plateau from the coastal regions and neighboring countries. In sharp contrast to the arid interior, the coastal regions outside this mountain ring, such as the strip bordering the Caspian Sea (which is 400 miles or 650 km long and never more than a certain width), benefit from the moisture trapped by the mountain barriers.
The Kuh-Rud Mountains: The Interior's Backbone
Among Iran's three major mountain chains, the Kuh-Rud Mountains span the interior of the country. This range, though less frequently highlighted than the Alborz or Zagros, forms a crucial backbone for Iran's central plateau. It consists of a series of isolated peaks and smaller ranges that rise from the desert plains, influencing local microclimates and providing isolated pockets of higher elevation that can support unique ecosystems.
The Kuh-Rud range is particularly significant for its role in the hydrological cycle of the interior, acting as catchments for seasonal rainfall that feeds into the internal drainage basins. These mountains also hold historical and cultural importance, with ancient trade routes and settlements often found nestled within their valleys, utilizing the natural protection and resources they offer.
The Caucasus and Eynali-Sahand Ranges
In the western part of Iran, specifically in the northwest, the influence of the Caucasus Mountains can be observed. While the main body of the Caucasus lies further north, its southernmost extensions contribute to the rugged terrain of Iran's historic Azerbaijan region. This area is characterized by a complex interplay of mountain ranges and river valleys.
Tabriz, a major city in this region, is situated in the Quru River valley, nestled between long ridges of volcanic cones in the Sahand and Eynali mountains. Tabriz's elevation ranges between 1,350 and 1,600 m (4,430 and 5,250 ft) above sea level, a testament to the city's mountainous surroundings. These volcanic mountains, particularly Sahand, are known for their picturesque landscapes and potential for winter sports.
Further west, near the Turkish border, lies the town of Maku, situated in a mountain gorge at an altitude of 1,634 meters (5,361 ft). Maku's location, just 22 kilometers (14 mi) from the Turkish border, highlights how Iran's mountainous terrain forms natural boundaries and strategic points. The presence of these diverse mountain systems across the country underscores the complex and varied nature of an Iran mountains map, each range contributing to the nation's unique geographical identity.
Mountains Shaping Iran's Climate and Life
The pervasive presence of mountains across Iran is not merely a topographical feature; it is the primary determinant of the nation's climate, biodiversity, and the very distribution of its population. Iran's topography is diverse and dominated by rugged mountain ranges, which define much of its landscape and create a multitude of microclimates.
These mountains enclose several broad basins, acting as natural barriers that trap moisture on one side and create rain shadows on the other. This phenomenon is clearly reflected in Iran's Köppen climate classification zones locator map, which shows a dramatic shift from humid, temperate climates near the Caspian Sea to arid and semi-arid conditions in the interior and southern regions. For instance, the Alborz range blocks moisture from the Caspian Sea, leading to lush forests on its northern slopes and much drier conditions on its southern, inward-facing slopes.
Similarly, the Zagros Mountains, stretching from the northwest to the southeast, create distinct climatic zones. The western slopes receive more rainfall, supporting a richer variety of vegetation, while the eastern slopes transition into the drier central plateau. This environmental variety supports distinctive ecosystems and agricultural zones throughout the country. Different crops thrive in different regions, from rice paddies in the Caspian lowlands to date palms in the warmer southern foothills of the Zagros.
The mountains also play a crucial role in providing water resources. Snowmelt from the high peaks feeds rivers and underground aquifers, which are vital for irrigation and drinking water in the arid regions. Historically, this has led to the development of unique water management systems, such as qanats, which tap into underground water sources from the mountains and transport them to villages and agricultural fields over long distances.
Furthermore, the mountains have influenced human settlement patterns. Typically, one major town has dominated each of the broad basins enclosed by mountains, benefiting from the natural protection and resources offered by the surrounding terrain. This close relationship between mountains and human life is a constant theme across Iran, making an Iran mountains map not just a geographical tool, but a window into the country's cultural and ecological fabric.
Exploring Iran's Mountainous Regions: A Traveler's Guide
For adventurers and nature enthusiasts, an Iran mountains map is an invitation to explore a world of breathtaking landscapes and challenging terrains. Iran boasts a long list of mountains above 4000m in different regions, particularly within the Alborz and Zagros ranges, offering diverse opportunities for trekking, climbing, and mountaineering. Surprisingly, even in the deserts of Iran, there are many mountains above 3000m, plus a few famous mountains above 4000m, presenting unique desert-mountain trekking experiences.
A detailed map of 20,705 Iran mountains shows not only elevation but also prominence, popularity, and difficulty, allowing enthusiasts to plan their adventures according to their skill levels. For example, clicking on a topographical map can display elevation data, providing crucial information for route planning. Whether you're a seasoned mountaineer aiming for the summit of Damavand or a casual hiker looking for scenic trails, Iran's mountains offer something for everyone.
Beyond the physical challenge, exploring these regions provides a deep dive into Iran's natural beauty and local cultures. Many mountain areas are home to nomadic communities, offering a glimpse into traditional ways of life. The environmental variety ensures that each region presents a unique experience, from the lush forests of the Alborz to the rugged, arid beauty of the Zagros.
For those planning a trip, resources such as a "Collection of Iran maps include tourist, geography, topography, railways, ancient, silk road, national parks, UNESCO sites, mountain & desert" are invaluable. These comprehensive maps, often available from established tourism and geography centers (like the one established in 2006, contactable at +98 21 26566026), can help navigate the vast and varied terrain. Additionally, utilizing online tools like Google Maps to find local businesses, view maps, and get driving directions can be incredibly helpful for accessing remote mountain areas.
It's important to remember that while the mountains offer incredible beauty, they also demand respect for their ruggedness. Proper preparation, including understanding the difficulty of routes and being aware of local conditions, is essential for a safe and enjoyable experience. Exploring an Iran mountains map is the first step in unlocking the adventure that awaits in this magnificent country.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Iran's Mountains
The majestic mountain ranges of Iran are far more than just geological formations; they are the very essence of the nation's identity, shaping its geography, climate, biodiversity, and cultural heritage. From the towering heights of Mount Damavand in the north to the expansive stretches of the Zagros in the west, an Iran mountains map vividly illustrates a landscape dominated by rugged peaks that have defined the country for millennia.
These mountains act as natural architects, separating basins and plateaus, dictating weather patterns, and fostering unique ecosystems that support a rich tapestry of life. They have influenced human settlement, trade routes, and the very character of Iran's diverse regions. Understanding the intricacies of Iran's mountainous terrain is crucial for appreciating its environmental resilience, its historical depth, and the enduring spirit of its people.
Whether you are a geographer, an adventurer, or simply curious about the world's diverse landscapes, the mountains of Iran offer a compelling subject for exploration. We encourage you to delve deeper into the topographical wonders of this ancient land. Have you ever explored the mountains of Iran, or do you dream of doing so? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, or consider sharing this article with fellow enthusiasts to inspire further discovery of Iran's magnificent peaks.
Iran Mountain Ranges - ADVENTURE IRAN Official Website - Iranian Tour

The map of Iran with the main mountains ranges, plains, counties and
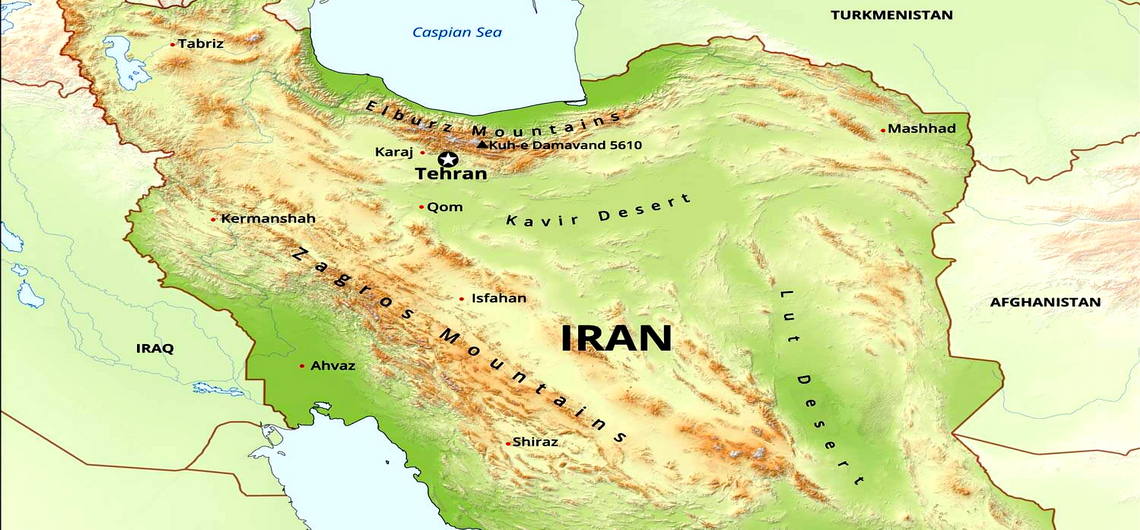
Iran Mountain Ranges - ADVENTURE IRAN Official Website - Iranian Tour