Unveiling Iran's Continental Home: Where Does Persia Truly Lie?
The Definitive Answer: Which Continent is Iran In?
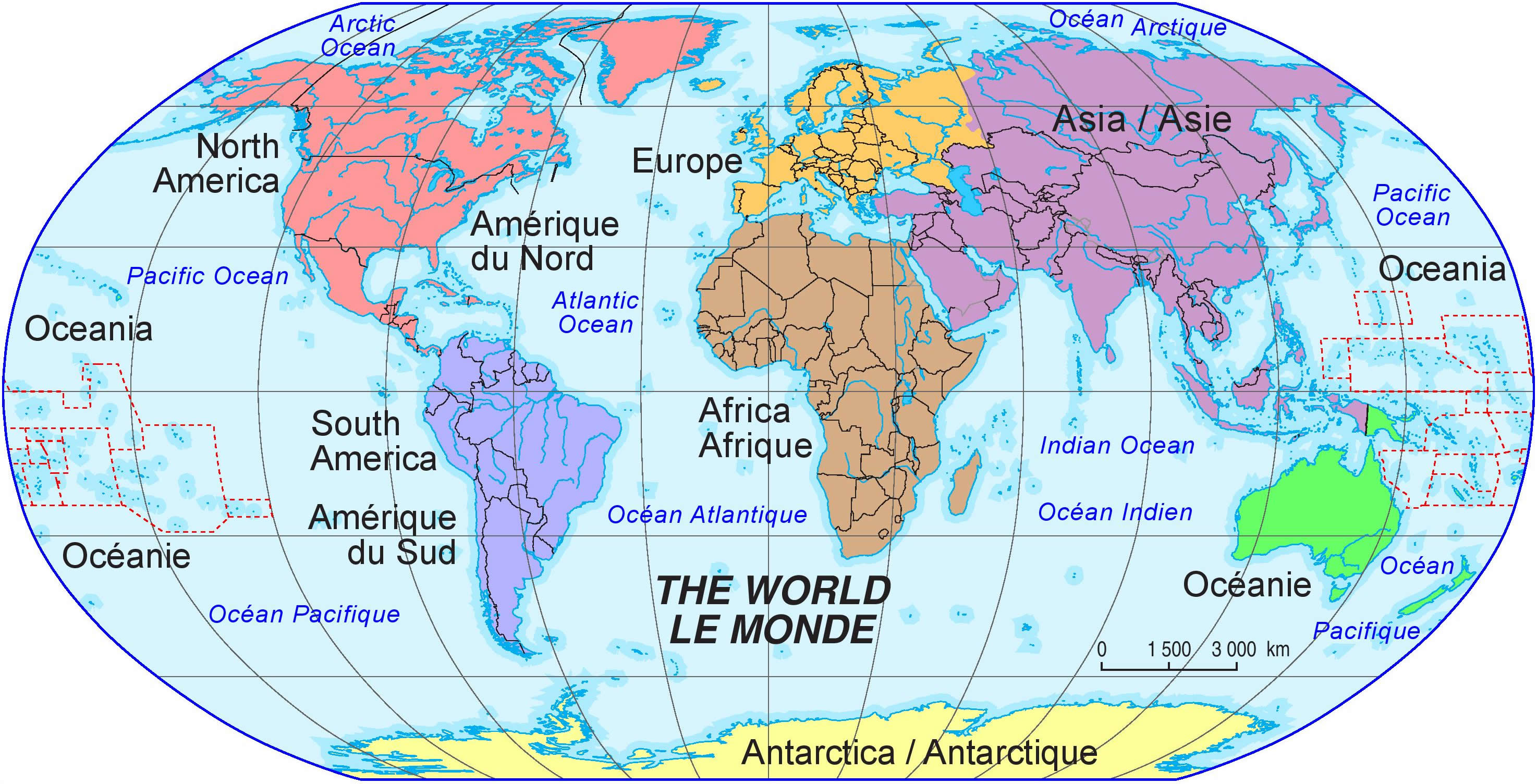
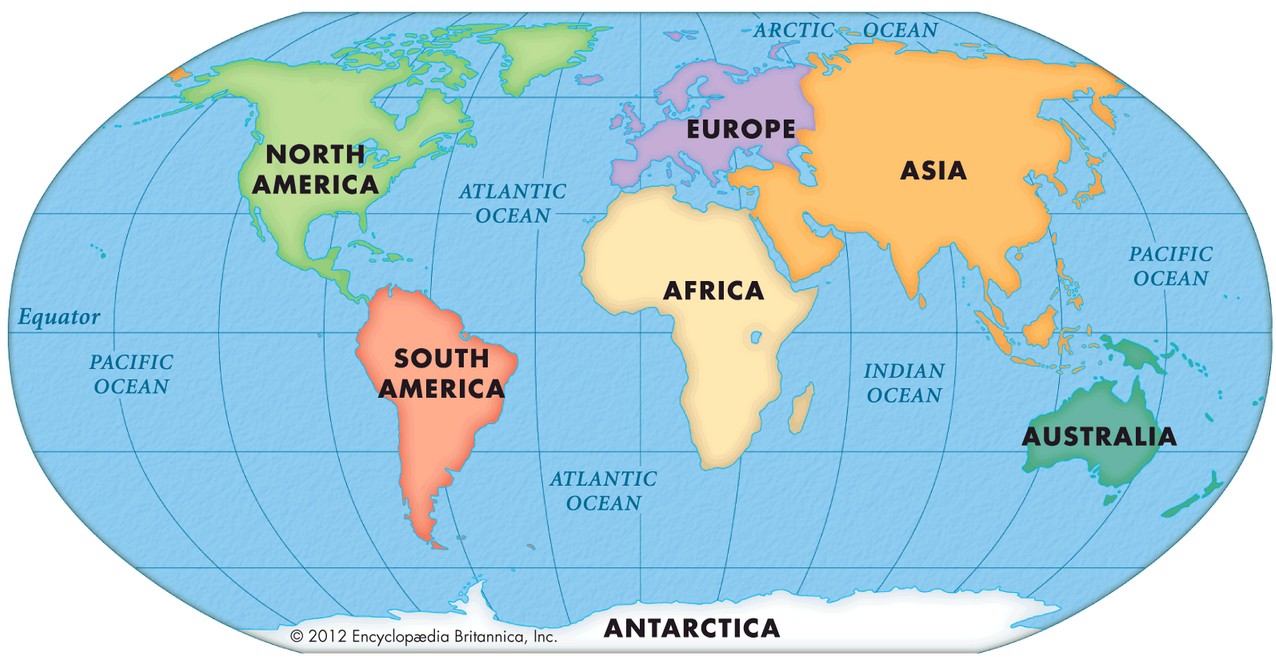
To put it unequivocally, Iran is located in the continent of Asia. More specifically, it is found in Western Asia, a region commonly known as the Middle East. While the term "Middle East" often evokes a sense of its own distinct geographical and cultural identity, it is crucial to remember that this region is traditionally considered an integral part of the larger Asian continent. Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI), firmly anchors itself within this vast and diverse landmass. Its placement in Western Asia is not merely a geographical label; it reflects centuries of historical, cultural, and economic interactions that have shaped Iran's unique identity within the broader Asian context. From ancient empires to modern geopolitical dynamics, Iran's destiny has been inextricably linked to its continental home. The question of which continent is Iran in, therefore, is answered with a clear and resounding "Asia."Geographical Coordinates and Hemispheric Placement
Understanding Iran's precise location on the globe offers further clarity regarding its continental affiliation. Iran is situated in the Middle East region at a latitude of approximately 32.427908 degrees North and a longitude of 53.688046 degrees East. These GPS coordinates paint a detailed picture of its global position. The latitudinal coordinate of Iran, 32.4279° N, places it significantly above the equator, firmly within the Northern Hemisphere. This northern placement contributes to its varied climate zones, from arid deserts to lush Caspian coastlines. Complementing this, its longitudinal coordinate of 53.6880° E positions Iran squarely in the Eastern Hemisphere. This dual placement in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres is characteristic of many Asian nations, reinforcing Iran's continental identity. The central part of the country is dominated by the vast Iranian plateau, a significant geographical feature that contributes to its diverse landscapes and climatic conditions, all within the Asian landmass.Iran's Vast Landmass and Strategic Borders
Iran is a country of immense scale, ranking as the second-largest nation in the Middle East by land area. Its total area is approximately 1,648,195 square kilometers (or 1.648 million square kilometers), a size comparable to, or slightly larger than, the state of Alaska in the United States. This vastness contributes to its varied nature and climate, supporting an abundance of plants and animals that are remarkable in both number and variety. The country's extensive borders are a testament to its pivotal position within Western Asia. Iran shares land boundaries with numerous nations, each contributing to its complex geopolitical landscape: * To the west, it borders Iraq and Turkey. * To the northwest, it shares borders with Azerbaijan and Armenia. * To the north, the vast Caspian Sea defines a significant portion of its boundary. * To the northeast, Turkmenistan lies adjacent. * To the east, Afghanistan and Pakistan form its eastern frontiers. * To the south, Iran is bound by the waters of the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, which connect it to global maritime routes. This intricate web of borders underscores Iran's role as a crossroads of civilizations and trade routes within the Asian continent, historically and presently. It is a mountainous, arid, and ethnically diverse country, characteristics often found across the expansive Asian landscape.The Middle East Context: A Regional Overview
While Iran is definitively in Asia, its classification within the "Middle East" often leads to questions about its precise continental location. The Middle East is a geopolitical and cultural region, not a continent itself. It typically encompasses seventeen nations and occupies an area of about 2,782,869 square miles. Geographically, the Middle East primarily sits within Asia, though its historical and cultural influence extends to parts of North Africa and southeastern Europe, leading to the occasional perception of it bridging three continents. However, when discussing the specific continental home of Iran, it is unequivocally Asia. The Middle East serves as a significant sub-region within the larger Asian continent, highlighting Iran's deep connections to its immediate neighbors while affirming its broader Asian identity.Historical Significance: Persia's Enduring Legacy in Asia
Iran, historically known as Persia, is often referred to as the heart of the Persian Empire of antiquity. This ancient civilization, with its roots stretching back to the 6th century BCE under Cyrus the Great, has profoundly shaped the history of Asia and beyond. The name "Persia" was used in the West since the beginnings of historical records associated with Cyrus the Great. The country's rich history has seen it play an important role in the region as an imperial power and as a factor in superpower rivalries, influencing vast swathes of the Asian continent. From the arrival of Hellenistic culture with Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE, which opened the gate to a long procession of foreign dynasties, to the Islamic Golden Age, Iran has been a crucible of cultural and intellectual development. The modern Iranian culture owes itself in part to a renaissance in the 8th century, a period of significant advancements in science, art, and philosophy that left an indelible mark across Asia. The Iran of today stands upon an ancient base of civilization and culture, a legacy deeply embedded within the historical narrative of the Asian continent. The question of which continent is Iran in becomes clearer when examining its historical trajectory, firmly rooted in Asian empires and cultural movements.Cultural Identity and Asian Roots
Culturally, Iran is an integral part of the Middle East, a region that, as previously noted, is traditionally considered within Asia. Its rich history, influenced by Persian civilization, Islamic heritage, and various other cultural elements, contributes to its unique identity within the continent. The Persian language (Farsi), distinct customs, and artistic traditions have spread and interacted with other Asian cultures for millennia, creating a vibrant tapestry of shared and unique heritage. This cultural depth reinforces Iran's belonging to Asia, demonstrating how its identity is intertwined with the continent's broader cultural landscape. The influences from the Indian subcontinent to Central Asia and the Levant all contribute to Iran's multifaceted cultural identity, firmly placing it within the Asian cultural sphere.Biodiversity and Natural Wonders: A Testament to Asian Diversity
Iran's vast geographical expanse and varied climate have endowed it with an astonishing array of biodiversity. The country contains abundant plants and animals, amazing in both number and variety, especially when compared to other parts of the world. This natural richness is a hallmark of the diverse ecosystems found across the Asian continent, which spans a wide range of climatic zones from deserts to high mountains and coastal plains. The Iranian vegetation diversity, for instance, is more than twice the size of the entire European continent and nearly equals that of the Indian subcontinent. This remarkable ecological wealth, supported by its varied terrain including the central plateau, arid regions, and mountainous ranges, underscores its position within Asia. The varied nature and climate found in Iran are typical of the immense geographical diversity characteristic of the Asian continent, further solidifying the answer to which continent is Iran in.Tehran: The Capital City's Asian Locale
The capital city of Iran is Tehran, a bustling metropolis situated in the northern part of the country. As the political, economic, and cultural heart of Iran, Tehran's location further emphasizes the nation's Asian identity. Its position within the northern reaches of the country, nestled against the Alborz mountains, is characteristic of many major cities across Asia, which often thrive in diverse geographical settings. The urban landscape, infrastructure, and cultural dynamics of Tehran are deeply rooted in its Asian context, reflecting the continent's rapid development and rich heritage.Navigating the Map: Visualizing Iran's Place
To truly grasp Iran's continental placement, visualizing its location on a world map is invaluable. When you examine an enlargeable map of the Islamic Republic of Iran, its position in Western Asia becomes immediately clear. The country's outline, bordered by the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south, unmistakably places it within the vast landmass of Asia. The GPS coordinates of Iran, as mentioned earlier, translate directly into this visual representation, confirming its latitude and longitude within the Asian framework. The provided outline serves as an overview and topical guide to Iran, reinforcing its geographical context. Its borders with neighboring Asian countries like Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan, trace lines across the Asian continent, illustrating the intricate connections and shared geographies that define this region.The Persian Gulf and Caspian Sea: Asian Waterways
Iran's maritime boundaries play a crucial role in defining its geographical and economic identity within Asia. To the south, Iran is bound by the strategic waters of the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. These bodies of water are vital for global trade, particularly for oil transport, and connect Iran to the Arabian Sea and the wider Indian Ocean, all within the Asian sphere of influence. To its north, the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water, forms another significant boundary. This sea is shared with other Asian and European countries, but for Iran, it firmly roots its northern frontier within the Asian continent, influencing its climate, culture, and economy. These waterways are not just geographical features; they are historical conduits that have facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and geopolitical interactions across Asia for millennia.Conclusion
In conclusion, the answer to **which continent is Iran** is unequivocally Asia. While it is a prominent nation within the Middle East region, this region itself is an integral part of the Asian continent, specifically Western Asia. Iran's geographical coordinates, its vast land area, its extensive borders with other Asian nations, and its rich historical and cultural heritage all firmly place it within this continent. From the ancient Persian Empire to its modern-day geopolitical significance, Iran's identity is deeply intertwined with the Asian landmass. We hope this comprehensive guide has clarified Iran's continental home and deepened your understanding of this remarkable nation's unique blend of geography, history, and culture. Do you have further insights or questions about Iran's geography or history? Share your thoughts in the comments below! If you found this article insightful, consider sharing it with others or exploring our other articles on global geography to continue your journey of discovery.- Evermore Orlando Resort
- Cody Garbrandt Girlfriend
- Michin Husband
- Matteo V Akoskin
- Corinna Dated And Related

Vector Map of World Bathymetry Continents | One Stop Map | World map
Carte du monde continent, la Carte du monde continent
Printable Continent Maps